Learning about computer basics means knowing that every device is a complete system. This system has physical parts and smart programs that work together. They make processing information fast and efficient.
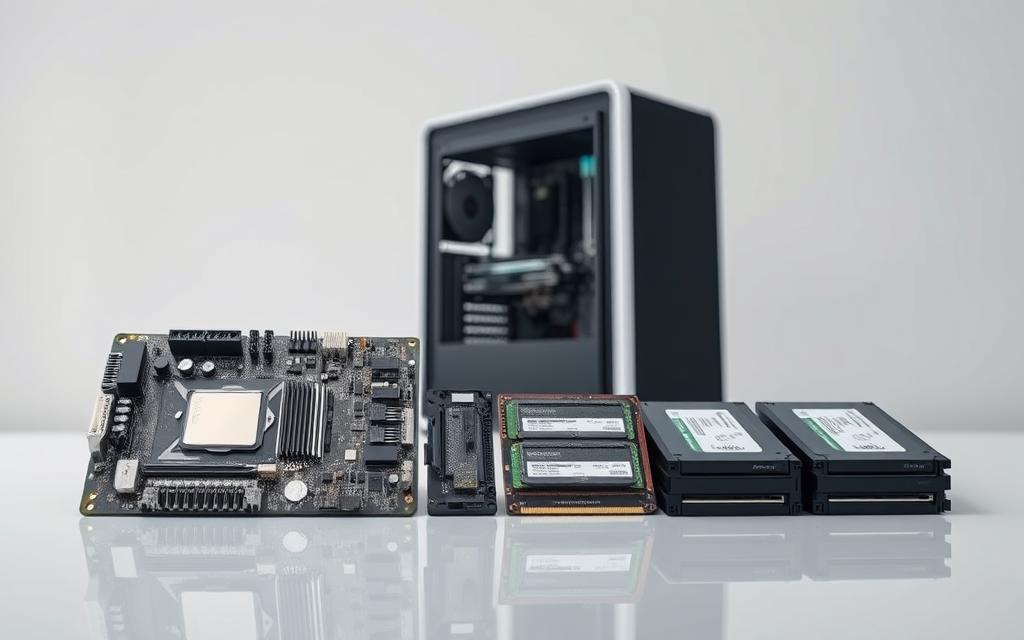
Looking at computer parts, you see both outside and inside elements working together. The parts you can see, like your monitor, keyboard, and mouse, are just a part of the whole setup.
If you’re starting with beginner computing, it’s key to know that the inside hardware and software are the heart of the system. They turn raw data into useful information by working together.
This computer components guide will show you the four key internal parts that make everything run smoothly. We’ll look at how each part helps your computer perform well and do its job.
Understanding Computer Systems: A Basic Overview
Every computing device works by combining physical parts and digital instructions. This partnership is key to modern computing systems.
What Makes Up a Computer?
Computers have two main parts: hardware and software. The parts you can touch and see are the computer hardware. This includes the central processing unit, memory, storage, and input/output devices.
The motherboard is the computer’s brain. It connects all parts, making them work together. It’s like the computer’s backbone.
The computer software adds instructions and functions. Operating systems like Windows or macOS manage the hardware. Applications let us do things like write documents or play games.
Why These Four Components Matter
The CPU, memory, storage, and input/output devices are vital. Each one has a special role in how the system works.
Memory lets the processor get data fast. Storage keeps information safe between uses. Input devices bring data in, and output devices show us the results.
This balance in computer architecture makes everything run smoothly. It handles simple tasks and complex ones, making our daily computing tasks possible.
What Are the Four Main Components of a Computer System?
Every computer system has four key parts that work together. These parts are the base of modern computing, from simple laptops to big servers. Knowing about these parts helps us understand how computers work and do tasks.
Defining the Core Elements
The four main parts make up a complete computer system. Each part does something different but works together. This teamwork lets computers do complex tasks well.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is like the brain of the computer. It runs instructions and does math. Modern CPUs have many cores for doing things at the same time.
The speed of the CPU is measured in gigahertz. This shows how fast it can process things. A faster CPU can handle more demanding tasks.
Memory (RAM)
RAM is where active programs and data are stored temporarily. It loses its contents when the power goes off. This makes data access very fast.
RAM’s main job is to give quick access to data that’s used a lot. Having more RAM means you can do more things at once and faster. Not enough RAM can slow things down.
Storage Devices
Storage devices keep data safe even when there’s no power. They hold things like operating systems, apps, and files. The amount of storage varies a lot.
There are different types of storage, like hard disk drives and solid-state drives. HDDs use moving parts, while SSDs use flash memory. Each has its own strengths in speed, size, and durability.
| Storage Type | Average Speed | Typical Capacity | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Disk Drive (HDD) | 100-150 MB/s | 1-10 TB | Mass storage |
| Solid State Drive (SSD) | 500-3500 MB/s | 250 GB-4 TB | Operating system |
| NVMe SSD | 3000-7000 MB/s | 500 GB-2 TB | High-performance tasks |
Input/Output Devices
Input/output devices let us interact with computers. They send data to the computer and get data back. This two-way communication makes computers useful.
Examples of I/O devices are keyboards, mice, monitors, and printers. They turn our actions into digital signals and back again. Without them, computers wouldn’t be able to communicate with us.
Each part is important for how we use computers. The CPU does the work, RAM provides space, storage keeps data safe, and I/O devices let us interact. Together, they make up a complete computer system.
The Central Processing Unit: The Brain of the Computer
The central processing unit is at the heart of every computer. It makes everything work smoothly. This microprocessor is the brain that understands and carries out instructions. Without it, computers are just useless pieces of hardware.
How the CPU Works
The CPU goes through a cycle of fetching, decoding, and executing instructions. It does this billions of times every second. This speed is what makes your computer quick to respond.
Key Functions: Arithmetic and Control
The CPU has two main parts. The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) does math and logical checks. The Control Unit makes sure instructions are followed and data moves where it needs to.
These parts work together to process information. The ALU does the math, and the Control Unit keeps things running smoothly.
Types of CPUs: Intel and AMD Examples
When picking a processor, people usually choose between Intel and AMD. The Intel vs AMD debate is common among desktop and laptop users. Both offer great products with their own strengths.
Intel Core Processors
Intel’s Core series includes i3, i5, i7, and i9 models. These processors are great for single-threaded tasks and gaming. They can reach speeds of 5.0 GHz or more in top models.
Intel uses Hyper-Threading to boost multitasking. This lets each core handle two threads at once.
AMD Ryzen Processors
AMD’s Ryzen series is a strong competitor to Intel. They offer more cores and threads at similar prices. Ryzen chips often hit speeds over 4.0 GHz across many cores.
AMD focuses on core count and parallel processing. This makes Ryzen good for tasks like content creation and productivity.
Both Intel and AMD keep improving. They push the limits of processor speed and efficiency. This competition is good for us, giving us better performance and value.
Memory: Temporary Data Handling
The CPU is like the brain of a computer. Memory is its workspace for active tasks and programmes. It’s where data is stored temporarily for quick access, making the system run smoothly.
Role of Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is where your computer’s active processes work. It’s different from permanent storage because it loses data when the computer turns off. This RAM function allows for fast data reading and writing.
When you open an app or file, it moves from storage to system memory. This makes it faster for the CPU to access, compared to getting it from storage every time.
How RAM Affects Performance
The amount and speed of RAM affect how well your computer handles tasks. More RAM means you can run more programmes without slowing down. Faster RAM gives the CPU quicker access to data, making everything run smoother.
For tasks like video editing, gaming, or running virtual machines, you need enough fast RAM. Without it, your system will use slower storage as virtual memory, slowing down a lot.
Types of Memory: DDR4 and DDR5
Computers mostly use DDR memory technology. DDR4 RAM has been common for years, with good performance and compatibility. It works at speeds from 2133MHz to 3200MHz.
DDR5 RAM is the latest memory technology. It has faster data transfer rates, better power efficiency, and more capacity than DDR4. But, it needs compatible motherboards and processors.
Common RAM Brands: Corsair and Kingston
Choosing memory from trusted brands is important. Corsair and Kingston are top memory brands, known for quality and reliability.
Corsair has a wide range of memory products, from basic to high-performance for gaming and overclocking. Kingston offers reliable memory at various prices, with their HyperX series being a favourite among enthusiasts.
Understanding these computer components helps when choosing memory. It’s about making the right choice for your needs and budget.
Storage: Long-Term Data Retention
Memory handles temporary data, but your computer needs permanent storage for when it’s off. This is where storage devices come in. They act as your computer’s digital filing cabinet for everything.
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) vs Solid State Drives (SSDs)
HDDs and SSDs are two main types of storage, each from a different era. HDDs have spinning magnetic platters and moving parts. SSDs use flash memory chips with no moving parts.
HDDs are great for big media collections because they’re cheaper and hold more. SSDs are faster and more durable, thanks to their lack of mechanical parts.
HDD Examples: Western Digital and Seagate
Western Digital makes reliable HDDs for everyday use and network storage. Their drives are a good mix of performance and price.
Seagate also makes HDDs for both home and business use. Their BarraCuda series is popular for desktops. They focus on high-capacity drives for backups and media.
SSD Examples: Samsung EVO and Crucial MX
Samsung’s EVO series is among the fastest consumer SSDs. They use advanced technology for fast data access.
Crucial’s MX series offers great value and performance. They use Micron’s NAND technology for reliable data retention and fast speeds.
How Storage Interfaces with Other Components
Storage devices work with other computer parts for smooth operation. When you start a programme, the storage device gets the files. Then, the CPU processes them from memory.
This process happens all the time while you’re using your computer. Faster storage means quicker programme loading and a more responsive system.
Your operating system lives on the storage drive. It’s the heart of your computer’s function. Without it, your system can’t boot or keep your files.
Input and Output Devices: Interaction with the Computer
Peripheral devices connect us to our computers. They let us interact with our machines. This interaction turns our commands into actions and shows us the results.
Common Input Devices: Keyboards and Mice
Input devices are key for telling our computers what to do. Keyboards and mice are the basics you find in most computers.
Today’s keyboards vary, from old-school membrane types to modern mechanical switches. Wireless tech has made our interactions with computers easier, without the mess of cables.
Examples: Logitech Keyboards and Microsoft Mice
Logitech keyboards are known for being comfy and working well. They often have special keys and lights for better use in any light.
Microsoft mice are great for precise tracking and are easy to hold for a long time. They have scroll wheels and extra buttons for quick navigation.
Common Output Devices: Monitors and Printers
Output devices show us what our computers are doing. Monitors display images, and printers make hard copies of digital files.
Screen tech has improved a lot. LCD and LED screens give clear images and use less power. Touchscreen monitors do both input and output at once.
Examples: Dell Monitors and HP Printers
Dell monitors are famous for their true colours and sharp pictures. They’re a top choice for graphic design and video editing.
HP printers are reliable for both home and office use. They range from small inkjet printers to big laser ones for businesses.
These devices make our computing experience better. The right mix of input and output devices boosts our work and happiness.
How the Components Work Together
Let’s look at how each part of a computer works together. This is what makes computing possible. It’s all about how these parts work together smoothly.
The Data Processing Cycle
Every computer action follows a basic pattern called the data processing cycle. This cycle has four main steps. It shows how data moves through your system.
First, input devices like keyboards and mice send data to the computer. The CPU then processes this data, using RAM as temporary storage. After that, the results go to output devices for you to see or use.
Lastly, the system might save the processed data for later. This data flow is at the heart of how computers work.
Real-World Example: Booting Up a Computer
The computer boot process is a great example of how components work together. When you press the power button, many parts start working at the same time.
At system startup, the CPU starts and looks for instructions in permanent storage. It finds the operating system files on your SSD or HDD and loads them into RAM.
As the OS loads, it connects with input and output devices. Your keyboard and mouse become active, and the monitor shows the startup sequence.
This whole process shows how all four components rely on each other. Without storage, the CPU has no instructions. Without RAM, processing is slow. Without I/O devices, you can’t interact with the system.
Conclusion
This summary shows how four key parts make up every modern computer. The Central Processing Unit is like the brain, handling tasks fast. Memory is for temporary work, and storage keeps your data safe.
Input and output devices help users interact with the computer. This makes the whole system work smoothly.
Knowing how these parts work together is key. Intel and AMD processors team up with DDR4 or DDR5 memory. Storage solutions like SSDs and HDs hold your files and operating system.
These elements talk to each other through the motherboard. This makes computing easy and efficient.
Understanding these basics helps users make better tech choices. Whether you’re building a PC or fixing problems, knowing how parts work is essential. For more info, check out these resources on computer architecture.
Learning these basics gives you a strong base in the digital world. You’ll be able to use technology with confidence and knowledge.
FAQ
What are the four main components of a computer system?
The main parts are the Central Processing Unit (CPU), Memory (RAM), Storage Devices, and Input/Output Devices. They help the computer process data, run programs, and talk to users.
How does the CPU function within a computer?
The CPU is the computer’s brain. It follows a cycle to execute instructions. It does math and logic and controls other parts to work well.
What is the difference between RAM and storage?
RAM is for tasks and programs that are being used. It’s fast for the CPU. Storage devices, like HDDs or SSDs, keep data safe even when off.
Why is RAM important for computer performance?
More and faster RAM means the computer can handle many tasks at once. It’s quick and efficient. Without enough RAM, the computer slows down.
What are the key differences between HDDs and SSDs?
HDDs are cheaper and hold more data. They use disks that spin. SSDs are faster and more durable. They’re pricier but better for speed.
Can you give examples of common input and output devices?
Input devices include keyboards from Logitech and mice from Microsoft. Output devices are monitors from Dell and printers from HP.
How do the four components work together in a computer system?
They work in a cycle. Input devices send data to the CPU. The CPU processes it with RAM. Results go to output devices, and data is saved on drives.
What role does the motherboard play in a computer?
The motherboard connects all parts. It lets the CPU, RAM, and storage devices talk to each other. This helps the computer work well.
Are there different types of CPUs available for consumers?
Yes, Intel and AMD are the main brands. Intel has the Core series, and AMD has Ryzen. They differ in speed and meet various needs.
What should I consider when choosing between DDR4 and DDR5 RAM?
DDR5 is newer and faster. It’s good for demanding tasks. But DDR4 is cheaper and reliable. Make sure your motherboard supports DDR5 or DDR4.